crop residue pellet mill
Agricultural Residue’s Annual Mount
Each year the amount of crop residue produced in the world is estimated at 2802x10(6) Mg/year for cereal crops, 3107x10(6) Mg/year for 17 cereals and legumes, and 3758x10(6) Mg/year for 27 food crops. The fuel value of the total annual residue produced is estimated at 1.5x10(15) kcal, about 1 billion barrels (bbl) of diesel equivalent, or about 7.5 billion bbl of diesel or 60 quads for the world. Such large amounts of agricultural residues are treated as waste and some of them are left to compost in the fields, but much of them are burnt out to clean the farm or field for planting other crops. Burning agricultural waste and crop residues may be an easy way but it is certainly not an economical way. What’s more, as environmental problem becomes more and more serious today, we should reduce and off-set anthropogenic emissions of CO(2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs) to mitigate the greenhouse effect. Consequently, the need for developing carbon (C) neutral and renewable sources of energy is more than ever before. Taking economical and environmental problems into consideration, making biofuel pellets from crop residue is a pretty good solution.
What is Crop Residue?
There are numerous types of agricultural cropping residues, such as: corn stalks, leaves, and sheaths; wheat straw; rice straw; barley straw; oat straw; seed grass straw; and bagasse from sugar cane. Here, one thing you should know that crop residue refers to crops’ parts that are not purposely obtained, and often they are just some kind of by-product of crops. For example, when sugar cane is grown for the bagasse, it is called an intentional or on-purpose crop and is no longer considered to be a residue. Only when you plant sugar cane for its juice or other purpose but not to get its bagasse, then sugar cane bagasse can be treated as a residue.
The primary agricultural crop residues in the world are wheat straw, rice straw, corn stalk and cotton stalk.
Wheat straw
Wheat is harvested almost all over the world, and its straw is an ideal agricultural residue for making biomass pellet fuel energy. Wheat straw’s lignin content is comparable to hardwoods and it has one of the highest cellulose contents of all of the agricultural fibers. When farmed intensively, wheat straw can be produced at a rate of 50 bushels/acre, yielding 1-3 tons per acre (depending on whether it is dry land or irrigated), and sold at a price of $20-45/ton.
Wheat straw is one of the most abundant non-wood plant materials available for making biofuel. Its conversion figure tends to be in the range of 1.0-1.1 tons of straw produced per ton of grain. However, estimates do have to be made with an eye to the specific type of residue used. Wheat, for example, tends to have a much higher straw residue yield than barley.
Rice Straw
Rice is the staple food for over half the world’s population and the second largest produced cereal in the world. Rice straw is another one of the so-called "cereal straws’. Rice straw contains a low concentration of lignin and has a higher silica content (as high as 18 percent in "clean rice straw," and 19-24 percent including silica from field dust) than other cereal straws. However, as rice is planted abundantly, rice straw is very easy and cheap to collect as raw material for making pellets, which can be used for heating or fuel in your own home. Thus making rice straw pellets is an economical way.
Here, one more thing about rice crop is that rice husk is also often used to make pellets. Get to know more about rice husk pellets and why make them.
Corn Stalk
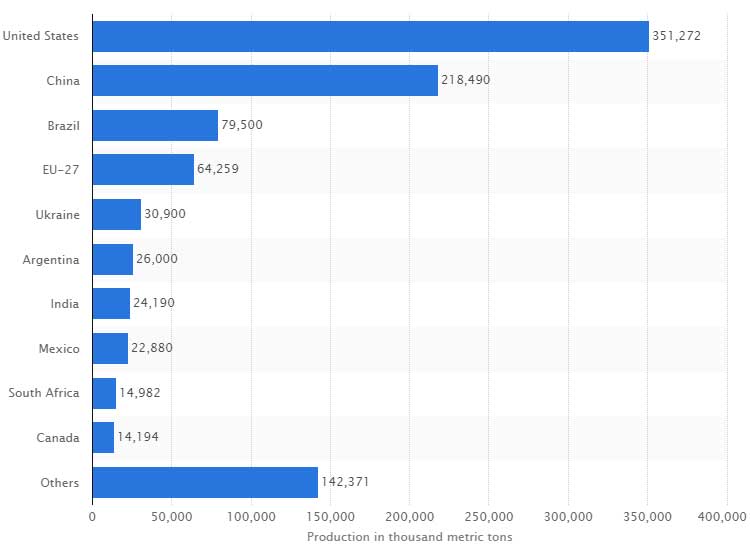
As pellet stove is more and more popular nowadays, making your own pellet fuel can save a lot of money. Pellet fuel can be made from any organic biomass including corn stalks. Because corn stalks are a byproduct of corn crops and not generally used after the corn is harvested, making pellet fuel from the stocks is an environmentally friendly solution for heating fuel. Corn is also widely planted worldwide. According to the official data, America produces the largest amount of corn last year (about 351,272 metric tons), followed by China and Brazil (shown as the chart below).
Cotton Stalk
Among crop residues, cotton stalk also takes a large share. The annual production capacity of cotton worldwide is about 25 million tonnes or 110 million bales, accounting for 2.5% of the world's arable land. Consequently, the amount of cotton wastes, mainly cotton stalk is rather large each year. Cotton stalk is the main biomass available in the field after the harvest of cotton, and its properties are as follows:
- higher heating value 15.83 MJ/kg;
- volatile 65.40%; ash 17.30%;
- carbon fraction 17.30%;
- C 39.47%, H 5.07%, O 39.14%, N 1.20%, S 0.02%, residue 15.10%, by the stoichiometric analysis of cotton stalks.

How to Make Crop Residual Pellets?
Making pellets from crop residuals is very economical and environmental friendly. And crop pellets have higher density and release more energy than crop residues. The machines you need depend on the crop residue's capacity and pellets output rate you want.
Small Pellet Mill for Individual Use
If the amount of crop residuals for making pellets is not very large, then a small crop residue pellet mill for home use is enough for you.

Before making pellets with small household pellet mill, you need to cut the crop stalks into short length. If you wouldn’t like to make this by hand, then a small hammer mill will save your trouble. After the size of crop residue is small enough, dry them in the sun and make sure that they have proper moisture content. Then put these raw material into the small flat die pelletizer, you’ll get your own desirable pellets for cooking or heating in the winter.
Large Pellet Mill & Pellets Line for Industrial & Commercial Use
If you are a rancher or have many lands that planted crops, you will get huge amount of crop residues, which are usually treated as agricultural waste. However, they can turn into treasure and bring you large benefits if made into pellets.

For large capacity, a large pellet mill, also known as ring die pellet mill is indispensable. The crop residue pellets making line usually contains the following machines: crusher, hammer mill, dryer, large industrial pellet mill, pellet cooler and pellets packing machine. Besides, transportation devices are also needed.
We receive enquiries in English, Español (Spanish), Русский язык (Russian), Français (French) and العربية (Arabic). Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!




